Rare Earth Element Series: SCANDIUM
Rare earth elements refer to Sc (scandium), Y (yttrium) and La~Lu (lanthanide elements) in Group IIIB of the periodic table, a total of 17 elements.
Dmitri Mendeleev (1834-1907) predicted the existence of scandium
Nilson (L.F.Nilson, 1840-1899) and Cleve (P.T.Cleve, 1840-1905) discovered scandium.

17 rare earth elements
Scandium is the highest-level transition metal with an atomic number of 21, but it was discovered later than its neighbors on the periodic table, and even among the rare earth elements. Scandium is an extremely dispersed and typically lithophile element, in the Earth's crust which is comparable to beryllium, boron, strontium, tin, germanium, arsenic, selenium, and tungsten. Unlike other rare earth elements, scandium lacks 4f electrons in its atomic structure and has a relatively small ionic radius. As a result, it does not exhibit the same close relationships with other rare earth elements and demonstrates relatively independent characteristics. There are over 800 minerals containing scandium, but as independent minerals of scandium, there are only a few, such as scandium yttrium ore, hydroxyapatite scandium ore, silicon scandium ore, and titanium silicate scandium ore. Their deposits are small, and rare in nature. The chemical properties of scandium are very active, and it is difficult to extract high-purity metals.
The process of enriching, separating, and extracting high-purity scandium from raw materials with complex composition and low scandium content is quite complicated, resulting in low scandium production and high prices. Despite the high price of scandium, it still does not stop people from exploring its applications. At present, the excellent properties of scandium still make it used in important fields such as electric light sources, aerospace, in electronics industry, nuclear technology, and superconducting technology.

● Classic Application 1: Scandium Oxide in Solid Electrolytes
Scandium oxide stabilized zirconia (ScSZ) replaces traditional yttrium oxide stabilized zirconia (YSZ) for solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), doubling the power density of SOFCs, which is a very promising new type of medium temperature solid electrolyte.
● Classic Application 2: Aluminum-scandium alloy targets are used in the field of electronic information
Aluminum-scandium alloy is used to prepare high-performance aluminum-scandium nitride piezoelectric films. As a new generation of piezoelectric materials. It can not only maintain high sound speed and high-temperature resistance but also significantly improve the piezoelectric coefficient, up to 3.5 times, while the bandwidth can be improved by 2.56 times, breaking through the performance of traditional aluminum nitride. It is applied to high-frequency filters, new micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) devices, and fingerprint recognition sensors. The key material for 5G communication, automotive chips, biomedicine, satellite communication, radar detection and other fields.
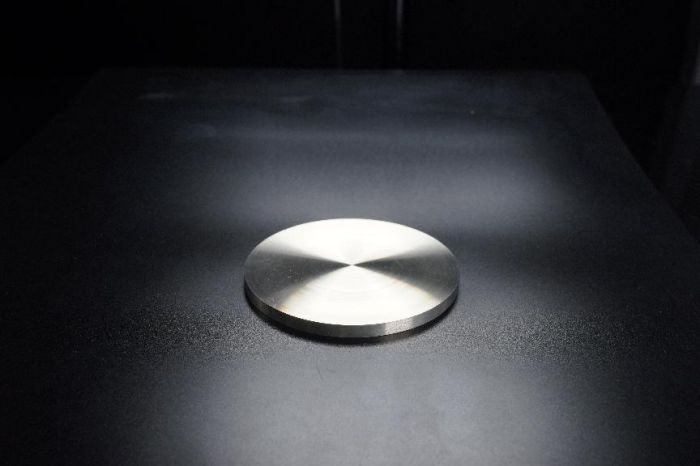

↑↑Aluminum-scandium alloy target
● Classic Application 3: Application of Scandium in Alloy Industry
Scandium in a single form is widely used in aluminum alloy doping. Adding a few thousandths of scandium to aluminum alloy will generate a new phase of Al3Sc, which will modify the aluminum alloy and significantly change the structure and properties of the alloy. Adding 0.2% to 0.4% Sc can increase the recrystallization temperature of the alloy by 150 to 200°C, significantly improving the high-temperature strength, structural stability, welding performance, and corrosion resistance, and can avoid the embrittlement phenomenon which is easy to occur during long-term work with high temperature. It has a very attractive development prospects in aerospace, aviation, ships, nuclear reactors, light vehicles, high-speed trains, and other fields.
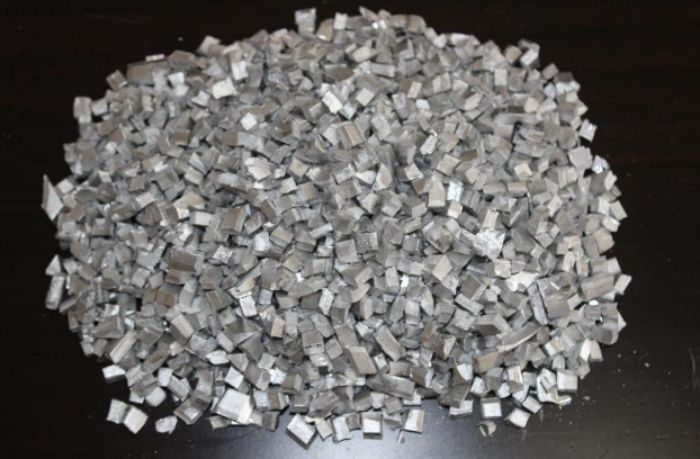

↑↑Aluminum-scandium alloy
Because scandium has a high melting point but its density is close to aluminum. It is also used in high-melting-point lightweight alloys such as scandium-titanium alloy and scandium-magnesium alloy. Due to its high price, it is only used in high-end manufacturing industries such as space shuttles.
The research on scandium-aluminum alloy has entered the practical stage. It is produced in Russia and has been widely used in aircraft manufacturing, while the United States uses it to produce various sports equipment.
Classic Application 4: Scandium is used in light sources, solar cells and atom tracer
The spectral line of scandium is 361.3~424.7nm, near-ultraviolet, and blue light, and the spectral line of sodium is 589.0nm and 589.6nm, two famous yellow light. The two spectral lines of scandium and sodium match just close to the sunlight. Scandium sodium lamps with the same illumination save about 80% of electricity compared to ordinary incandescent lamps, have a service life of 5000~25000h, and are called the third generation of light sources.
Scandium is also used in solar cells. In metal-insulator-semiconductor silicon photovoltaic cells and solar cells, scandium is the best barrier metal with an efficiency of 10% to 15%.
The scandium is used as a gamma ray source or 46Sc, an artificial radioactive isotope. Usually, we extract 45Sc from minerals, which is the only natural isotope of scandium.

 EN
EN NL
NL FR
FR DE
DE JA
JA KO
KO PT
PT RU
RU ES
ES TR
TR