High-Strength ZM7 Cast Magnesium Alloy
ZM7 is a magnesium-zinc-silver-zirconium alloy. Due to the high mass fraction of the strengthening element zinc, which is 7.5% to 9%, and the mass fraction of the precipitation hardening element silver, which is about 1%, this alloy has the highest tensile strength, yield limit and plasticity among the existing cast magnesium alloys in China at room temperature, and it also has good fatigue resistance. This alloy has good filling performance while it has a relatively large tendency of micro-porosity, corresponding process measures adopted during casting to overcome this issue. This alloy is used for parts that require high mechanical properties at room temperature.
I. Chemical Composition and Properties of ZM7 Alloy
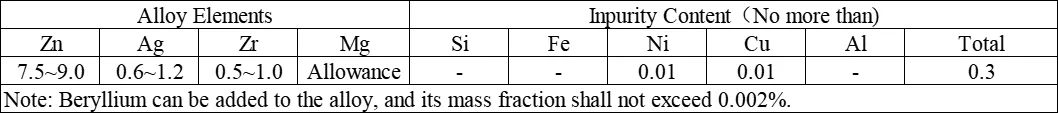
Chemical composition and impurity content (mass fraction) % of ZM7 cast magnesium alloy
(1) The oxidation resistance of ZM7 alloy is similar to that of other magnesium alloys. It is flammable and explosive, and has a relatively high risk.
(2) ZM7 alloy has good corrosion resistance in dry air, but its chemical stability is poor in humid air, water (especially seawater), and it reacts vigorously with most inorganic acids. In industrial atmospheres, the corrosion resistance of magnesium is similar to that of medium carbon steel. The oxide film of magnesium is not dense, so it must be surface treated before long-term use in the atmosphere.
(3) ZM7 alloy is stable to selenic acid, fluorides, and hydrofluoric acid, forming insoluble salts. Unlike aluminum, magnesium alloys do not react with caustic alkali and are also stable in gasoline, kerosene, and lubricating oil. Magnesium is one of the most electronegative metals, and it is not allowed to be directly in contact with aluminum alloys (except aluminum-magnesium alloys), copper alloys, steel, and other parts during assembly, otherwise it will cause electrochemical corrosion.
(4) The corrosion stability of magnesium alloys will be reduced by Iron, silicon, copper, nickel, chlorides, and other impurities as well as certain casting defects. Zirconium in the alloy can eliminate the harmful effects of impurities and refine the grain, thereby greatly improving the corrosion resistance of the alloy.
II. Physical Properties of ZM7 Alloy
ZM7 alloy is non-magnetic; its density ρ is 1.87 g/cm³; the melting temperature range is 475 - 621°C. The specific heat capacity and thermal conductivity of ZM7 alloy are shown in the following table. The coefficient of linear expansion is also presented in the table below.
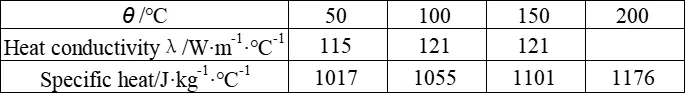
The specific heat capacity and thermal conductivity of ZM7 alloy

The coefficient of linear expansion of ZM7 alloy
III. Mechanical Properties of ZM7 Alloy
The shear strength τ of ZM7 alloy in T6 condition is 240 MPa. The typical tensile properties of ZM7 alloy at room temperature as per the technical standard (single cast specimen) are shown in the following table. The mechanical properties at room temperature and various temperatures are presented in the following table. The tensile properties at room temperature of ZM7 alloy castings with different cross-sections are shown in the following table. The high-temperature tensile properties are presented in the following table. The tensile properties of ZM7 alloy after heating at 150°C for 50 hours are shown in the following table. The hardness of ZM7 alloy castings is presented in the following table. The impact properties of ZM7 alloy are shown in the following table. The high-temperature fatigue limit of ZM7 alloy is presented in the following table. The room temperature elastic modulus of ZM7 alloy castings is presented in the following table.
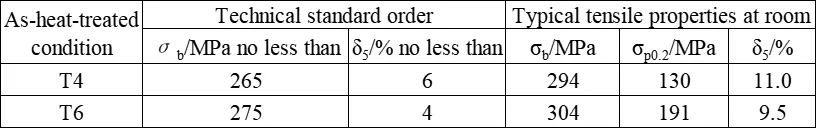
Technical standards for ZM7 alloy (single-cast specimens) and typical room-temperature tensile properties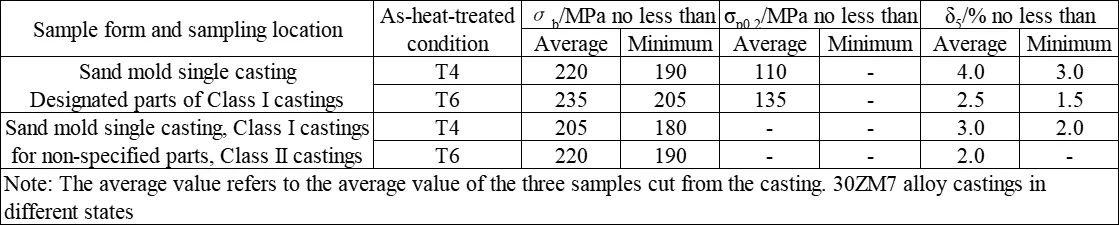
Mechanical property values of ZM7 alloy castings in different conditions
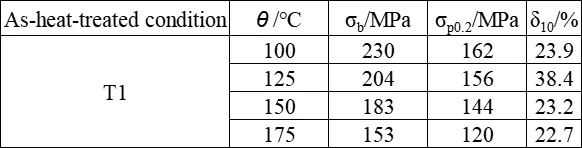
Typical high-temperature tensile properties of ZM7 alloy castings
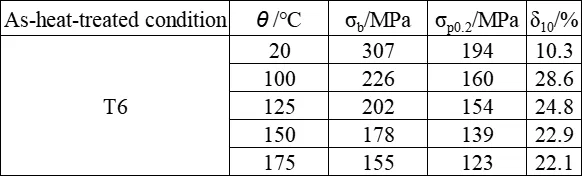
Tensile properties of ZM7 alloy after heating at 150℃ for 50 hours
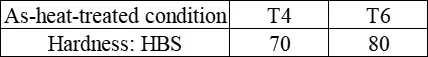
The hardness of ZM7 alloy castings
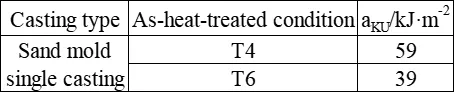
The impact performance of ZM7 alloy
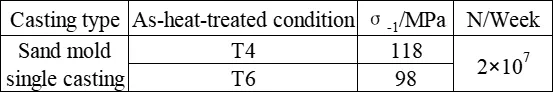
The high-temperature fatigue limit of ZM7 alloy
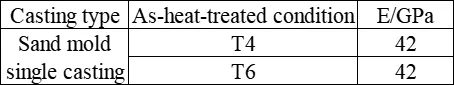
The room-temperature elastic modulus of ZM7 alloy castings
IV. Melting and Casting Process of ZM7 Alloy
Melting:
(1) The melting and casting process of this alloy is similar to that of other magnesium-zinc-zirconium alloys. Zinc and silver are added in the form of pure metals, while zirconium is added in the form of magnesium-zirconium master alloy.
(2) During the alloy preparation process, it is necessary to avoid contamination by elements such as aluminum, iron, silicon, and manganese, as these elements hinder the grain refinement effect of zirconium on the alloy.
(3) Due to the low solubility of zirconium and its tendency to form compounds with various impurity elements and thus be lost, the amount of zirconium added must be 3 to 5 times the required zirconium content in the alloy to ensure the zirconium content in the alloy. The high zinc content in the alloy makes the addition of zirconium somewhat difficult, so the melting technology and temperature control are extremely important.
Casting Process:
(1) Casting performance. The alloy has good filling properties but a significant tendency towards microscopic porosity. The first crack in the hot cracking tendency test was formed at a ring width of 17.5mm. The linear shrinkage rate is 1.1%. Casting temperature: 720-800℃.
(2) Welding performance. The alloy has poor welding performance and is generally difficult to weld.
(3) Heat treatment process performance. Castings should be used in the solution-treated (T4) or solution-treated and artificially aged (T6) state. During solution treatment, the atmosphere in the heat treatment furnace should contain 0.7% (at least 0.5%) sulfur dioxide (0.5-1.5kg of pyrite or ferrous sulfide must be added per cubic meter of furnace volume) or 3% carbon dioxide as a protective atmosphere to prevent oxidation and combustion of magnesium castings. When placing castings on the heat treatment rack, care should be taken to avoid warping deformation of the castings. Special fixtures or supports may be necessary when required.
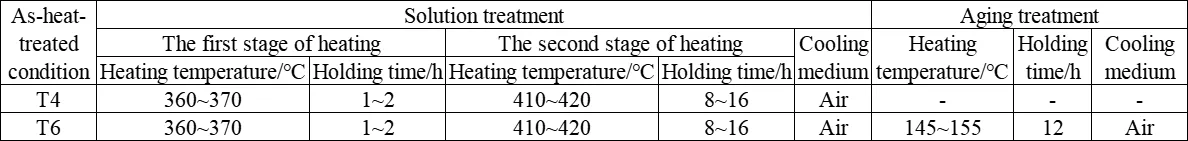
Common heat treatment processes for ZM7 alloy castings
V. Applications of ZM7 Alloy
ZM7 alloy has been used in parts such as wheel hubs and outer cylinders, and can also be applied to simple-shaped stressed components.

 EN
EN NL
NL FR
FR DE
DE JA
JA KO
KO PT
PT RU
RU ES
ES TR
TR

